Swimming is widely recognised as an excellent form of physical exercise that caters to all ages and fitness levels. It engages nearly every muscle group and provides a full-body workout that can enhance cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and flexibility. Moreover, swimming is considered a low-impact activity that reduces the strain on joints, making it a sustainable option for maintaining fitness over a lifetime.
The benefits of swimming extend beyond physical health, positively impacting mental wellbeing as well. Engaging in regular swimming sessions has been linked with improved mental health, including reductions in stress and anxiety. The rhythmic nature of swimming, combined with the soothing effect of water, can lead to a meditative state, promoting relaxation and mental clarity. Additionally, swimming has been associated with improved sleep patterns, which is a crucial component of good mental health.
Research also suggests that people who swim regularly may enjoy a longer life span, as well as a reduced risk of chronic illnesses. Participation in swimming can help individuals manage their weight, improve coordination and balance, and even enhance cognitive function. As a social activity, swimming can provide opportunities for interaction and community building, fostering a sense of belonging and support that is vital for holistic wellbeing.
Physical Health Benefits of Swimming
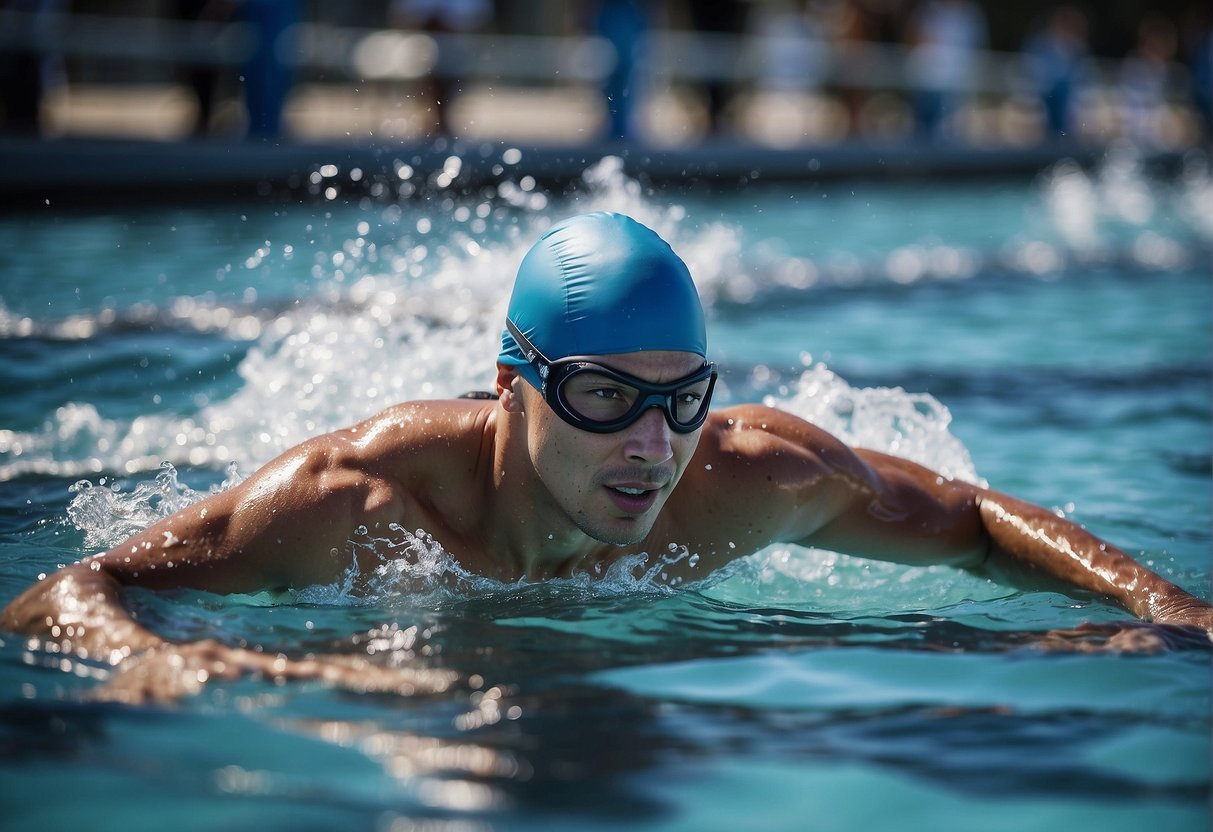

Swimming is a comprehensive activity benefiting various aspects of physical well-being. It is instrumental in enhancing cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and offering weight management benefits.
Cardiovascular Fitness and Heart Health
Swimming is an excellent exercise for the cardiovascular system. Regular swimming increases the heart rate and improves circulation, which can lead to a reduction in the risk of heart disease and stroke. It can also help lower blood pressure and improve heart health over time.
Muscle Strength and Tone
The resistance of water during swimming means that multiple muscle groups work simultaneously. This can lead to improved muscle strength and tone, especially in the shoulders, back, abdominals, legs, hips, and glutes. It’s an effective form of strength training without the need for weights.
Flexibility and Mobility
Unlike many forms of exercise, swimming enhances joint flexibility and mobility. The low-impact nature of swimming allows those with arthritis or osteoporosis to exercise without added stress on the joints, thereby improving their range of motion.
Weight Management
Swimming burns calories effectively, which can be beneficial for maintaining or losing weight. Engaging in this form of exercise can help combat obesity by utilising major muscle groups and providing a vigorous whole body workout.
Alleviating Health Conditions
Regular swimming has a positive impact on various health conditions including diabetes, asthma, and multiple sclerosis. By providing a low-impact, high-resistance workout, swimming can help manage symptoms and improve overall health outcomes for individuals with these conditions.
Mental Health and Cognitive Benefits

Swimming is a powerful exercise which taps into multiple aspects of mental health and cognitive functions. It not only offers a way to improve mood and alleviate stress but also plays a significant role in battling anxiety and depression. On top of these benefits, swimming also contributes to enhanced brain health through increased blood flow and the stimulation of endorphins.
Stress Reduction and Mood Improvement
Regularly taking to the pool facilitates the release of endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones. This biochemical process is critical for improving mood and providing a sense of relaxation and satisfaction. The consistent rhythm and soothing properties of water also promote a meditative state, further reducing stress levels and enhancing mental clarity.
Combating Anxiety and Depression
Swimming is a form of physical activity that has been linked to reductions in the symptoms of anxiety and depression. The aerobic nature of swimming increases blood flow to the brain and can lead to a decrease in stress-related hormones, creating a more balanced psychological state. The therapeutic effect of being submerged in water can make it a particularly beneficial exercise for those with anxiety, as detailed in a Swim England report.
Enhanced Brain Health
The mental health benefits of swimming extend to the long term, including potentially slowing cognitive decline in ageing populations. Research has found that physical activities like swimming could help in lowering the risk of dementia and aid in maintaining overall brain health. With the boost in blood circulation and oxygen supply to the brain during a swim, individuals can experience improvements in cognitive function and memory recall.
Benefits for Specific Groups

Swimming is a versatile activity that offers specific health benefits for varied demographic groups. From aiding in the healthy development of children to providing therapeutic benefits for older adults with long-term health conditions, the advantages of swimming are tailored to the needs of different ages and abilities.
Children and Swimming
Children reap significant health benefits from swimming. It is an essential skill that boosts physical development and improves cognitive function. Engaging in swimming lessons can accelerate their growth in physical, cognitive, and social skills. Regular participation in swimming can establish a foundation for a lifelong enjoyment of physical activities, promoting overall well-being.
Swimming for Older Adults
For older adults, swimming presents a low-impact way to stay physically fit and sharpen their mental acuity. Evidence suggests that older people who swim regularly can maintain their health and manage long-term health conditions more effectively. This form of exercise is beneficial in maintaining strength, flexibility, and even contributes to a dementia-friendly lifestyle.
Prenatal and Postnatal Health
Swimming is a recommended form of exercise for pregnant people. It offers a safe way to maintain fitness and can help manage pregnancy-related discomfort. Postnatal swimming aids post-menopausal women and new mothers alike in regaining strength and improving mood, without placing undue stress on the body.
Inclusive Swimming for Disabilities
Inclusion in swimming is critical for people with disabilities, providing both physical and psychological benefits. Accessible swimming programmes are designed to be dementia friendly and accommodating to various impairments. Through personalised delivery that caters to individual needs, swimming can become a tool for inclusive health and well-being, fostering autonomy and empowerment for all participants.
Safety and Accessibility Considerations

In addressing the integration of swimming into one’s lifestyle, attention should be paid to ensuring safe practices and accommodating diverse needs for access in aquatic environments.
Understanding Risks and Preventing Injuries
Swimming is a low-impact activity enjoyed by many; however, it is not without its risks. Understanding these risks is vital to ensuring safety in the water. Areas of concern include the potential for drowning or injury due to improper technique or accidents. Adult swimming lessons can play a significant role in injury prevention, teaching correct form and enhancing water confidence. Additionally, community pools should enforce safety protocols and have lifeguards on duty to minimise the risk of death or injury.
- Key Safety Tips:
- Never swim alone or without a lifeguard present.
- Participate in swimming lessons, regardless of age.
- Follow pool rules and signage.
Accessibility for Aquatic Activities
Ensuring accessibility in aquatic activities is crucial for inclusive community engagement. Individuals with disabilities or those who are less mobile should have the opportunity to experience the benefits of aquatic activity. Facilities that offer accessible entry points, such as ramps or lifts, empower these community members to participate safely. Moreover, the provision of tailored programmes for different abilities enhances the inclusivity of nature-based and traditional swimming environments.
- Features to Improve Accessibility:
- Ramps and handrails for pool entry.
- Specialised equipment, like pool wheelchairs or flotation devices.
- Programmes for different skill levels and physical capabilities.
Enhancing Overall Wellbeing
Swimming is a holistic activity with multiple facets that contribute significantly to a person’s overall wellbeing. It encompasses not only the physical health benefits but also boosts psychological and social health by enhancing quality of life and fostering connections.

Quality of Life and Lifelong Wellbeing
Swimming consistently contributes to a better quality of life, with evidence showing that those who swim may enjoy a longer lifetime. Swimming is a form of exercise that benefits the cardiovascular system and improves muscle strength throughout the body. This, in turn, promotes lifelong wellbeing, as regular physical activity is associated with reduced risk of chronic diseases. The report on Health and Wellbeing Benefits of Swimming aligns with this by stating that swimmers live longer and that older individuals who engage in swimming maintain better mental and physical health.
Community and Social Engagement
The social aspect of swimming is highly beneficial. Engaging in swim activities like water aerobics classes or joining a swim team can lead to enhanced community and social bonds. The capacity of swimming to unite individuals from all walks of life provides a unique avenue for social engagement, offering a supportive environment that bolsters mental health. This communal activity can alleviate feelings of loneliness and depression, as suggested by the content found on Swim Your Way to a Better Life: 20 of the Best Benefits of Swimming.
Connection with Nature
Swimming in natural bodies of water such as the sea or lakes can deepen one’s connection with nature, enhancing mental wellbeing in a unique manner. Being immersed in water and surrounded by the natural landscape can provide a sense of tranquillity and can serve as a grounding experience. As noted by Six ways swimming benefits your mental wellbeing, interactions with outdoor water environments can have inherently positive effects on an individual’s mental wellbeing, releasing endorphins and providing a natural boost to mood.
Types of Swimming Strokes and Their Benefits

Swimming is not only an enjoyable activity but also a comprehensive workout routine that engages multiple muscle groups. Different strokes focus on various aspects of health and fitness, offering a range of benefits to swimmers.
Freestyle and Efficiency
Freestyle, often referred to as the front crawl, is synonymous with swimming efficiency. This stroke is characterised by an alternating arm movement and a continuous flutter kick. It is well-regarded for its speed and the full-body workout it provides, effectively enhancing cardiovascular endurance and improving muscle strength across the body. Consistent practice of freestyle can lead to improved posture and flexibility.
Backstroke for Back Health
The backstroke relies on inverse movements to those used in freestyle, with swimmers facing upwards. It promotes a healthier spine by encouraging a straighter posture during the stroke. The mechanics of the backstroke can contribute to a reduction in back pain and are beneficial for aligning the vertebral column which in turn may alleviate posture-related problems.
Breaststroke and Joint Health
Breaststroke is unique, with its synchronous underwater arm motion and frog kick. This stroke is gentler on the joints, making it suitable for people of all ages and those with joint concerns. It can improve joint flexibility, particularly in the hips, legs, and shoulders, while also providing a moderate cardiovascular workout.
Butterfly Stroke for Upper Body Strength
The butterfly stroke is a more advanced and intensive swimming style, abundantly engaging the muscles of the upper body. It requires simultaneous overhead arm movement along with a powerful dolphin kick. Regularly swimming the butterfly stroke can lead to greater upper body strength and can enhance the strength and endurance of core muscles. It demands good coordination and is beneficial for those looking to intensify their swimming workouts.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Swimming into Your Routine

Swimming, an excellent form of physical activity, offers a multitude of health benefits ranging from improved endurance to mental wellbeing. This section provides targeted advice for those looking to embrace swimming as a key component of their fitness regimen.
Starting Out with Swimming
For beginners, it’s imperative to start slowly and build up the duration of swimming sessions incrementally. Initially, one might aim for a minimum of three swimming sessions per week, gently increasing the intensity and duration as confidence and fitness levels elevate. As one’s comfort in the water improves, experimenting with different strokes can enhance the enjoyment of the activity and work various muscle groups.
Sustainable Swimming Practices
To maintain swimming as a long-term exercise habit, it’s crucial to keep practices sustainable. This can be achieved by setting realistic goals, tracking progress through a swim journal or app, and ensuring each session ends with a cool-down to aid recovery. Additionally, integrating swimming into one’s weekly regime can be as simple as preparing swim gear the night before to minimise morning delays. Swimming can also serve as a relaxing activity, so considering a visit to the spa post-exercise could contribute to overall wellbeing.
Combining Swimming with Other Exercises
Swimming complements other forms of exercise like cycling or running, offering a low-impact alternative that helps reduce stress on joints while still improving cardiovascular health. On non-swim days, incorporating cycling can provide a balanced workout routine that aligns with one’s endurance goals. Furthermore, using swimming as an active recovery practice on rest days assists not just in physical recuperation, but also in mental relaxation, providing a holistic approach to fitness.
Frequently Asked Questions

Swimming is a multifaceted form of exercise that provides numerous health and wellbeing benefits, ranging from improved mental health to better cardiovascular fitness.
What are the mental health benefits of regular swimming?
Swimming is highly beneficial for mental health, as it has been shown to reduce stress levels and improve mood. It stimulates the release of endorphins, natural brain chemicals that evoke feelings of happiness and relaxation.
In what ways does swimming benefit cardiovascular health?
Regular swimming is an efficient way to enhance cardiovascular health. It raises heart rate without putting too much stress on the body, improves blood flow, and can lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
How does engaging in swimming influence body composition?
Engagement in swimming can lead to improved body composition by increasing muscle mass and reducing body fat. The resistance offered by water during swimming means that multiple muscle groups are worked simultaneously, helping to tone the body and increase metabolic rate.
What advantages does swimming offer for emotional wellbeing?
Swimming offers significant advantages for emotional wellbeing. It can foster a sense of accomplishment and increase self-esteem. Many find the experience of being in water inherently soothing, which may contribute to emotional balance.
Can daily swimming positively impact one’s overall fitness level?
Daily swimming can have a profound impact on overall fitness levels. It is an effective form of aerobic exercise that improves endurance, flexibility, and strength due to its full-body workout nature.
What are the physical health benefits associated with swimming?
The physical health benefits of swimming include improved joint mobility, reduced risk of chronic illnesses such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and enhanced musculoskeletal strength. It provides a low-impact workout, which is beneficial for those with arthritis or injuries.